Confined Space Safety
Explore the pivotal role of Intrinsically Safe Technology in hazardous work environments for enhanced industrial safety. Read our detailed overview.
Between 2011 and 2018 there were 1,030 fatal occupational injuries involving workers in confined spaces in the United States. The largest number of fatalities occured in these three sectors:
Between 2011 and 2018 there were 1,030 fatal occupational injuries involving workers in confined spaces in the United States. The largest number of fatalities occurred in these three sectors:
What does it mean to work in a confined space?
Working in confined spaces is performing tasks or duties in enclosed or partially enclosed areas, with limited means of entry or exit. These spaces are not designed for continuous occupancy and can pose various hazards to workers.
Confined spaces can include:
- Tanks
- Vessels
- Silos
- Storage bins
- Vaults
- Pits
- Manholes
- Tunnels
- Pipelines
- And other similar areas. Read more
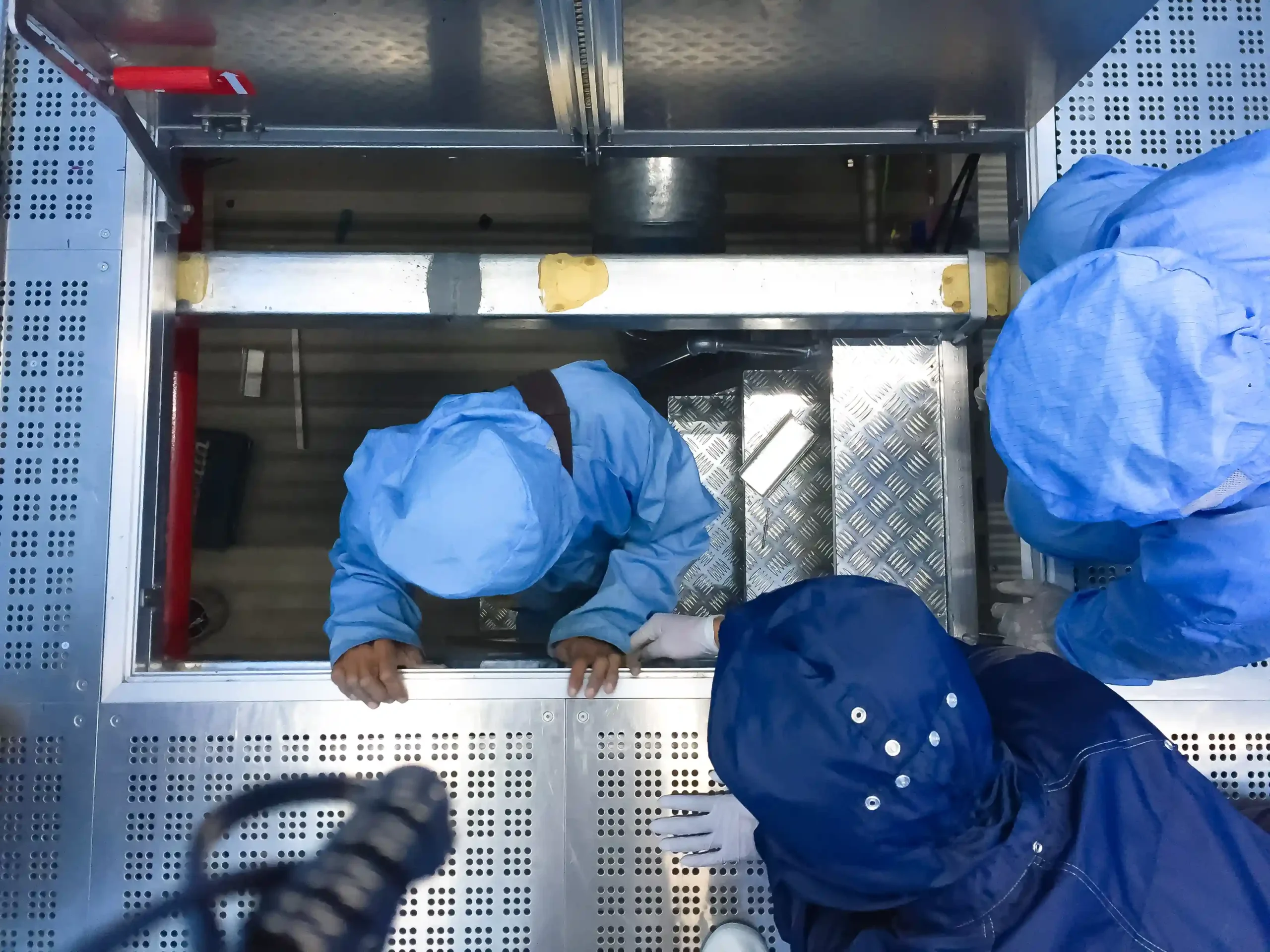

What does it mean to work in a confined space?
Working in confined spaces is performing tasks or duties in enclosed or partially enclosed areas, with limited means of entry or exit. These spaces are not designed for continuous occupancy and can pose various hazards to workers.
Confined spaces can include:
- Tanks
- Vessels
- Silos
- Storage bins
- Vaults
- Pits
- Manholes
- Tunnels
- Pipelines
- And other similar areas. Read more

Unique risks arise in this type of work environment. Common hazards associated with confined spaces include:
Limited Exit and Entry
Confined spaces often have small openings or restricted access points, making it challenging for workers to enter and exit swiftly during emergencies such as fires, gas leaks, or structural collapse.
Poor Ventilation
Restricted airflow in confined spaces can lead to a buildup of hazardous gases, vapors, or airborne contaminants, posing risks of asphyxiation, suffocation, or respiratory problems for workers.
Physical Hazards
Confined spaces may contain physical obstacles such as sharp edges, moving machinery, electrical hazards, or unstable structures, increasing the risk of slips, trips, falls, or crushing injuries.
Engulfment
Some confined spaces, such as grain bins or storage silos, present the risk of engulfment in materials like grain, sand, or water, which can rapidly trap and suffocate workers.
Temperature Extremes
Confined spaces may experience temperature extremes, including excessive heat or cold, which can lead to heat stress, hypothermia, or frostbite, depending on the environment.
Communication Challenges
Limited visibility and restricted access in confined spaces make communication difficult, hindering effective coordination among workers, supervisors, safety managers, and emergency responders.
Rescue Difficulties
When an accident or emergency happens, rescuing workers from confined spaces can be complex and time-consuming due to the confined nature of the environment, potentially delaying medical assistance and exacerbating injuries.
Risk Assessments
Employers conduct thorough risk assessments before any work begins in a confined space. This involves identifying potential hazards such as toxic atmospheres, limited entry or exit points, and physical hazards like moving parts or engulfment risks.Training
Workers undergo comprehensive training on confined space entry and safety procedures. This includes understanding the specific hazards associated with confined spaces, proper use of equipment, emergency procedures, and rescue techniques.Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is crucial to ensure the air quality within confined spaces remains safe for workers. Ventilation systems may include natural ventilation, mechanical ventilation, or the use of air movers and fans to exchange air and remove contaminants.Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Workers are equipped with appropriate PPE based on the identified hazards. This may include respiratory protection for toxic atmospheres, protective clothing, harnesses, and other equipment to prevent injuries. While beneficial, this can also create a heat stress hazard.Confined Space Entry Procedures
Clear procedures for entering and exiting confined spaces are established and followed rigorously. This includes obtaining necessary permits, securing the area, testing atmospheric conditions, and implementing safe entry and exit practices.Atmospheric Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of the atmospheric conditions inside confined spaces is conducted to detect any changes or hazards. This involves using gas detectors and other monitoring devices to measure oxygen levels, flammable gases, and toxic substances.Physiological Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of workers’ physiological status inside confined spaces is conducted to alert on heat stress and fatigue. This involves using wearable sensors to provide real-time heart rate and core body temperature data.Regulatory Compliance
Employers adhere to relevant regulations and standards set by organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), including OSHA’s Confined Space Entry standards (29 CFR 1910.146). Compliance ensures that minimum safety requirements are met and helps prevent accidents and legal liabilities.Emergency Response Plans
Comprehensive emergency response plans are in place to address potential accidents or incidents. This includes procedures for rescue and evacuation, communication protocols, and training for emergency responders. By implementing these safety practices and regularly reviewing safety protocols, employers can effectively mitigate risks for workers in these environments.Our product has been integrated seamlessly into many organizations across multiple industries: utility, manufacturing, alternative energy, environmental remediation, military training, first responders, healthcare, construction and more.
How our solution helps
Going beyond traditional methods of ensuring safety when it comes to heat illness, SlateSafety’s solution offers and array of features and benefits to make your safety program easy and efficient while also helping to prevent heat stress incidents before they happen.
Real-Time Physiological Monitoring and Alerts

Configurable Threshold Analytics
</br

TapAlert
No Movement Detection

Real-Time Physiological Monitoring and Alerts

TapAlert

No Movement Detection

Configurable Threshold Limits

Real-Time Physiological Monitoring and Alerts

Configurable Threshold Limits

TapAlert

No Movement Detection

Customer Feedback
“Allowing us to monitor heat stress/philological health. It is hard for us to keep track of work/rest cycles. People get busy and lose track. These help us keep everyone accountable for safe operation.”
Spencer Riccio
Industrial Hygiene Specialist at Advansix
Privacy and Security
Your privacy and security are paramount to SlateSafety. We’ve implemented rigorous measures to safeguard organizations and individuals, ensuring that their sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access. Our commitment to prioritizing security underscores our dedication to providing a safe and trusted platform for all users.
Customer Feedback
“Allowing us to monitor heat stress/philological health. It is hard for us to keep track of work/rest cycles. People get busy and lose track. These help us keep everyone accountable for safe operation.”
Spencer Riccio
Industrial Hygiene Specialist at Advansix
Privacy and Security
Your privacy and security are paramount to SlateSafety. We’ve implemented rigorous measures to safeguard organizations and individuals, ensuring that their sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access. Our commitment to prioritizing security underscores our dedication to providing a safe and trusted platform for all users.
