Imagine working in an environment where the air feels like a thick, hot blanket, suffocating every breath and drenching you in sweat. This is not just uncomfortable but a potentially serious health risk known as heat stress. Now, imagine there’s a way to measure and manage this risk effectively. That’s where Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) comes into play. This article explores WBGT, why it matters and how organizations can apply it to protect their workers from the dangers of heat.
What is Wet Bulb Globe Temperature
Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) is a measure designed to encapsulate the combined effects of air temperature, humidity, wind speed, and visible and infrared radiation on the human body. This composite temperature is instrumental in providing a more accurate reflection of the heat stress experienced by individuals compared to traditional measures like the heat index.
The uniqueness of WBGT lies in its consideration of not just the temperature but also the cooling effect of wind and the impact of solar and thermal radiation on the body. By integrating these variables, WBGT offers a comprehensive assessment of the environmental conditions contributing to heat stress, making it an invaluable tool for workplace safety in high-temperature environments.
The History of WBGT
The development of the WBGT index in the 1950s marked a significant advancement in the field of occupational health and safety. Originally crafted for the United States Marine Corps; its creation was motivated by the need to protect military personnel from the risks of heat stress during rigorous training and operations in diverse and often extreme climates.
Since then, WBGT has gained widespread acceptance as a critical standard for heat stress management across various industries. Its evolution from a military-specific solution to a universal benchmark underscores its effectiveness in safeguarding workers from the dangers of heat exposure.
Why WBGT Matters
As global temperatures rise and heatwaves become more frequent, the potential for heat-related illnesses in the workplace is a growing concern. Heat stress, if not properly managed, can lead to severe health issues such as heat stroke, dehydration and even fatalities.
Moreover, it can significantly impair worker productivity and concentration, leading to increased errors and accidents. By providing a realistic measure of heat stress, WBGT enables employers to implement effective heat safety protocols, ensuring the well-being of their workforce while maintaining operational efficiency.
Utilizing WBGT as a guide, organizations can tailor their operations to mitigate heat risks. This includes scheduling work during cooler parts of the day, designing work-rest cycles that allow for adequate recovery and ensuring access to cooling areas and sufficient hydration. Furthermore, WBGT readings can inform the selection and use of personal protective equipment that helps maintain core body temperature within safe limits.
Having established the critical role of WBGT in addressing heat-related challenges in the workplace, it’s essential to explore the components that make up this crucial index. Understanding these elements sheds light on how WBGT provides a comprehensive measure of heat stress.
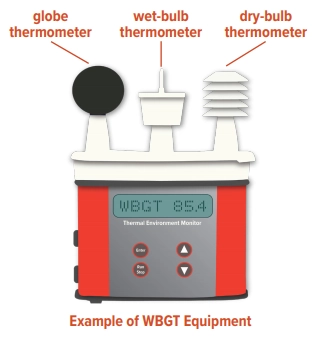
Components of WBGT
Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) equipment uses three critical environmental factors to assess heat stress risk, uniquely capturing the thermal environment affecting human comfort and health.
- Natural Wet-Bulb Temperature: This component is essential for understanding the cooling effect of evaporation on the body. Measured with a thermometer covered in a water-soaked cloth and exposed to airflow, it reflects the temperature, humidity, and the body’s potential for evaporative cooling. In high humidity conditions, where the air is saturated with moisture, the evaporation rate decreases, leading to higher perceived heat stress.
- Globe Temperature: Measured with a globe thermometer, this component gauges the amount of radiant heat present, which can significantly affect the heat stress levels. The thermometer is encased in a hollow, black globe that absorbs radiant heat from sunlight or other sources, mimicking the heat absorption by the human body. This measure is crucial in environments where direct sunlight or significant radiant heat sources (like furnaces or machinery) are present, as it influences the body’s ability to dissipate heat.
- Air Temperature: The most straightforward of the three measures the ambient air temperature using a standard thermometer. While it is the most commonly understood indicator of heat, on its own, air temperature does not fully represent the heat stress risk. It does not account for humidity, wind speed, or radiant heat, which significantly affects human heat perception and stress.
Calculating the Impact
Integrating these three components into the WBGT index provides a comprehensive view of the thermal environment’s impact on individuals. Each piece is measured using specific, purpose-designed instruments that ensure accuracy and reliability:
- The natural wet-bulb temperature is measured with a sling psychrometer or a similar device that can accurately reflect the evaporative potential of the environment.
- The globe temperature requires a globe thermometer, typically a black sphere that can absorb radiant heat, placed in the area where the assessment is conducted to measure the radiant heat accurately.
- Air temperature is measured with a standard mercury or digital thermometer, providing the baseline temperature of the environment.
These measurements are then weighted and combined according to a formula that accounts for their relative contributions to heat stress. The specific weighting can vary depending on the setting (e.g., indoor vs. outdoor) and the activities performed. For example, in direct sunlight, the globe temperature carries more weight due to the significant impact of solar radiation on heat stress.
The WBGT index provides a holistic approach to heat stress, enabling more effective thermal risk management in various settings. With a clearer understanding of WBGT’s components, let’s examine how to apply this information to workplace safety protocols.
WBGT in Workplace Safety
WBGT helps organizations take a strategic approach to mitigating heat stress risks. These guidelines are a benchmark for adjusting work/rest cycles, particularly in environments where high temperatures can significantly impact worker health and safety.
For instance, in construction or agricultural sectors where outdoor work is prevalent, WBGT guidelines help determine the maximum duration workers should be exposed to the heat. In foundries where high ambient temperatures are compounded by radiant heat from machinery, WBGT guidelines are critical.
Developing Safety Protocols
By integrating WBGT readings into their safety protocols, companies can proactively manage the health risks of working in hot conditions. This involves adjusting the duration and intensity of work based on current WBGT levels and implementing hydration breaks to prevent dehydration.
For example, a policy might dictate that when the WBGT reaches a certain threshold, outdoor work is limited to 45 minutes, followed by a 15-minute rest break in a shaded or air-conditioned area. Moreover, these safety protocols can include guidelines for acclimatization, gradually increasing exposure to heat over a period to help workers’ bodies adapt, thus reducing the likelihood of heat-related illnesses.
Real-World Application
The practical application of WBGT in workplace safety can be seen in a wide range of industries, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness. In manufacturing, companies can use WBGT readings to redesign their workspaces, incorporating ventilation systems that reduce ambient temperature and humidity. WBGT can also modify training schedules, ensuring that the most physically demanding activities happen during cooler parts of the day.
In oil and gas extraction operations, where indoor and outdoor work environments can present significant heat stress risks, WBGT is instrumental in developing rotational work schedules. These schedules ensure workers spend a controlled amount of time in high-heat areas before being rotated out, allowing their body temperature to normalize in cooler rest areas equipped with hydration stations.
The strategic application of WBGT in managing workplace safety leads to significant benefits. By adhering to these guidelines, organizations can protect their workforce from heat-related illnesses, enhance productivity and safety, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
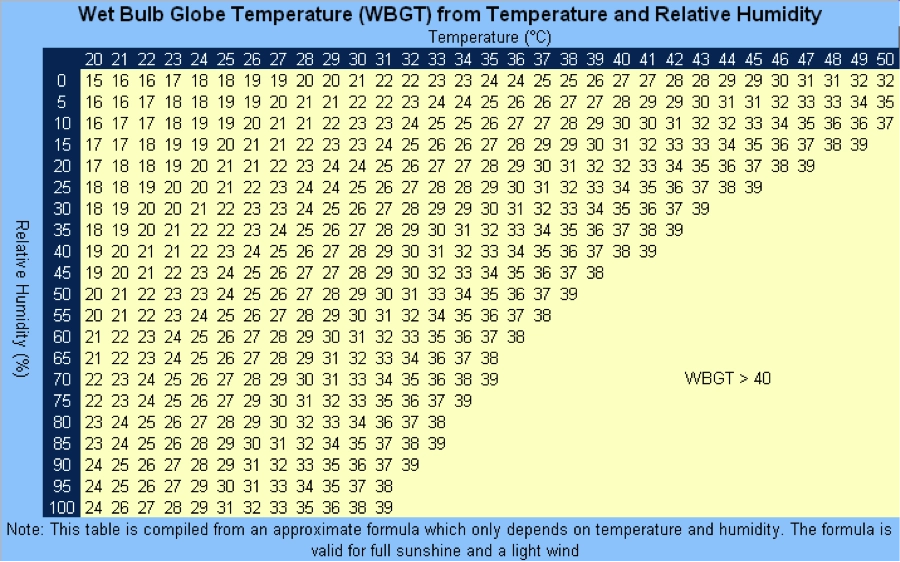
Source: Korey Stringer Institute
Benefits of WBGT
Adherence to WBGT guidelines is a frontline defense against heat-related health issues, from mild heat exhaustion to life-threatening heat stroke. Companies can significantly mitigate the risk of these conditions by carefully monitoring WBGT levels and adjusting work practices accordingly.
This proactive approach is particularly beneficial in industries with outdoor work or high-temperature environments, such as construction, agriculture, and certain manufacturing sectors. Implementing WBGT-based guidelines ensures that workers are not exposed to unsafe heat levels for prolonged periods. As a result, heat-related illnesses can be dramatically reduced, safeguarding worker health and well-being.
Enhanced Productivity and Safety
Utilizing WBGT readings for informed decision-making allows companies to maintain not just the safety but also the productivity of their workforce. In extreme heat conditions, worker efficiency can decline by up to 78%, and the risk of accidents can increase due to heat-induced fatigue and cognitive impairment.
By optimizing work/rest cycles and ensuring adequate hydration, businesses can help keep their employees alert and physically capable, even in challenging conditions. This enhances individual performance and contributes to the overall operational efficiency and safety of the workplace.
Compliance
Many jurisdictions have specific guidelines or regulations addressing heat stress in the workplace, and failure to comply can result in substantial fines, litigation, and reputational damage. WBGT can help organizations stay on the right side of these complex legal and regulatory requirements related to occupational heat.
By integrating WBGT into their health and safety protocols, companies can ensure they meet these requirements, protect themselves from legal consequences, and affirm their commitment to worker safety. However, while the benefits of using WBGT to manage heat stress are undeniable, it’s crucial to acknowledge the system’s challenges and limitations.
Challenges and Limitations of WBGT
One of the main difficulties of using WBGT lies in the variability of environmental conditions, which can change rapidly and affect the accuracy of WBGT readings. For instance, sudden shifts in weather, such as cloud cover or wind speed, can dramatically alter the thermal environment, necessitating constant monitoring and adjustment of work practices.
Additionally, the effectiveness of WBGT is contingent on the availability and proper use of specialized equipment to measure its components accurately. This can present logistical challenges, particularly in remote or resource-limited settings. The need for additional assessments, such as individual health evaluations and acclimatization status, further complicates the implementation of WBGT guidelines.
Moreover, while WBGT provides a valuable framework for assessing heat stress risk, it may not capture all factors affecting individual susceptibility to heat-related illnesses. Personal risk factors, such as age, medical conditions, medication use, and acclimatization level, can influence an individual’s response to heat and are not directly accounted for by WBGT alone.
The above challenges highlight the need for a multifaceted strategy. A strategy that combines WBGT with personal risk assessments, adaptive management practices, and cutting-edge technological solutions to ensure the safety and well-being of all workers.
SlateSafety’s Innovations
SlateSafety‘s innovations stand at the forefront of modern heat safety solutions. The BAND V2 and BEACON V2 devices exemplify how integrating environmental and physiological monitoring can create a comprehensive safety ecosystem.
These tools go beyond measuring ambient conditions; they assess individual physiological responses to heat, such as heart rate and core body temperature, providing a personalized safety alert system. This dual approach ensures that both environmental factors and personal susceptibility to heat stress are accounted for, enabling more targeted interventions and adjustments to work practices.
How SlateSafety’s Products Complement WBGT in Heat Safety
Integrating SlateSafety’s products with WBGT guidelines adds layers of real-time data and physiological insights, thus offering a multifaceted approach to heat stress management. Here’s how:
- Real-time Data and Alerts: The capability to provide instant feedback on heat stress conditions enables immediate action to prevent heat-related illnesses. For instance, if a worker’s core body temperature rises dangerously, the BAND V2 can trigger an alert, prompting immediate intervention.
- Monitoring of Physiological Signs of Heat Stress: By continuously tracking physiological markers, SlateSafety’s devices identify early signs of heat stress that might not yet be evident through environmental measurements alone. This early detection system allows for proactive measures, such as additional rest breaks or hydration, before a worker’s health is compromised.
- Integration with Environmental Readings: Combining SlateSafety’s physiological monitoring with traditional WBGT environmental readings ensures a comprehensive view of heat stress risks. This integration allows safety professionals to adjust workloads, schedules, and protective measures based on a complete assessment of both the environment and the worker’s condition.
By leveraging the strengths of both WBGT and advanced monitoring technology, companies can achieve unparalleled protection against heat stress, fostering a safer and more productive working environment for all employees. Don’t let heat stress put your team at risk; contact SlateSafety today. Experience the peace of mind from knowing you’re not just meeting but exceeding heat safety standards, ensuring your workforce is protected, productive, and thriving, even in the most challenging conditions.

