A few commonly known ways to prevent heat illness during work in hot environments are keeping cool, staying hydrated and taking the time to rest and recover. Besides these basic tips, tools like Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT), heat index calculators and wearable physiological monitors provide a more in-depth way to monitor and analyze conditions. Using all the tools available helps to prioritize worker safety without decreasing productivity.
What is Wet Bulb Globe Temperature Monitoring?
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), WBGT is a measure of heat stress in direct sunlight. WBGT takes into account these factors: temperature, humidity, wind speed, sun angle and cloud cover. It is used as a safety measure for individuals who work or exercise outdoors in direct sunlight.
WBGT is calculated using this equation:
WBGT=0.7Tw+0.2Tg+0.1Td
Tw = wet bulb temperature (humidity)
Tg= globe temperature (radiant heat)
Td= dry air temperature
How Does Wet Bulb Globe Temperature Monitoring Help Prevent Heat Illness and Injury?
A WBGT device measures the perceived temperature considering the factors listed above to determine safe levels of exposure and exertion dependent on weather and work environment and the Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) recommends using them.
WBGT devices are particularly useful to get an accurate read of the five factors at industrial facilities and outdoor worksites. These devices have three types of thermometers and should be placed near the worksite, in direct sunlight (if work will be performed in direct sunlight).
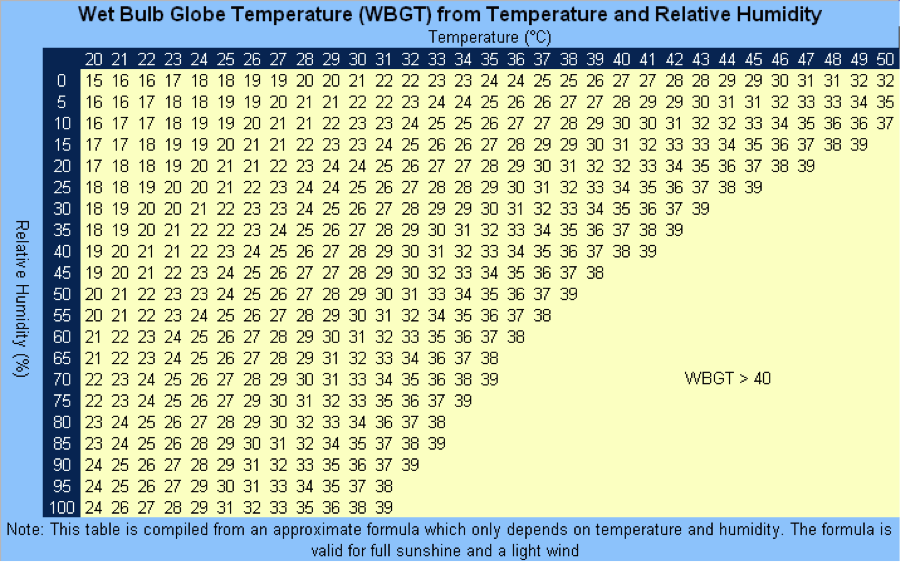
WBGT charts are available as an alternative to a device, however, they only account for full sunshine and light wind conditions, and not any additional factors that may need to be considered. Because of this, the number on the chart may not be an accurate representation of the actual conditions.
Additionally, WBGT monitoring can help to establish proper work and rest cycles to ensure workers are safe and have time to recuperate before getting back to work again. Having this advanced measure can help increase productivity while preventing heat illness and injury at the worksite.
Free online tools to measure WBGT in your area:
What is the difference between WBGT and heat index?
Heat index is another important tool when it comes to heat safety. It is widely accepted that the WBGT is more effective when it comes to managing work and rest cycles because it is more in-depth and considers more factors than the heat index.
Heat index is measured in the shade and only takes into account air temperature and relative humidity. This leaves out the other environmental factors measured by the WBGT: wind speed, sun angle and cloud cover. Heat index devices are available as well as online heat index calculators.
Free resources to monitor heat stress and safety:
What other tools are available to help prevent heat illness and injury?
Physiological monitoring has come a long way in recent years and it can be a great way to supplement WBGT monitoring for increased worker safety. SlateSafety’s BAND V2 is an arm-worn wearable device that provides real-time data. With configurable alert thresholds, an organization can decide when to alert workers or onsite safety supervisors. Alerts are triggered when workers are overexerted and need a break, then notifications can be sent when they’re rested and ready to return to work. Exertion levels, heart rate and core temperature are key indications that are monitored. Thresholds can be customized to your organization or you can choose the ACGIH® loadout for guidelines on physiological monitoring.
Sources:
https://ksi.uconn.edu/prevention/wet-bulb-globe-temperature-monitoring/#
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/heatstress/heatapp.html

